In the dynamic world of electronics manufacturing, innovation knows no bounds. One such revolutionary advancement is the utilization of conductive ink in screen printing—a technique that is reshaping the landscape of electronic product design and production. In this article, we delve into the fascinating realm of screen printing with conductive ink, exploring its diverse applications, the advantages of systematic automation, and the intricate process of ink curing.
Applications Galore: Products Printed with Conductive Inks
The applications of conductive ink extend far beyond conventional electronic circuitry. From flexible displays and wearable technology to smart packaging and medical devices, the versatility of conductive ink allows for the creation of intricate electronic components on various substrates, including paper, plastics, and textiles.
One of the most notable applications of conductive ink is in the realm of printed electronics. This burgeoning field leverages the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of printing technologies to produce lightweight, customizable electronic devices. Printed sensors, antennas, and RFID tags are just a few examples of the products empowered by conductive ink printing, offering novel solutions in industries ranging from healthcare to automotive.
Moreover, conductive ink opens doors to the realization of innovative concepts such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices and flexible electronics, where traditional manufacturing methods fall short. With conductive ink, designers and engineers can unleash their creativity, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in electronic product design.
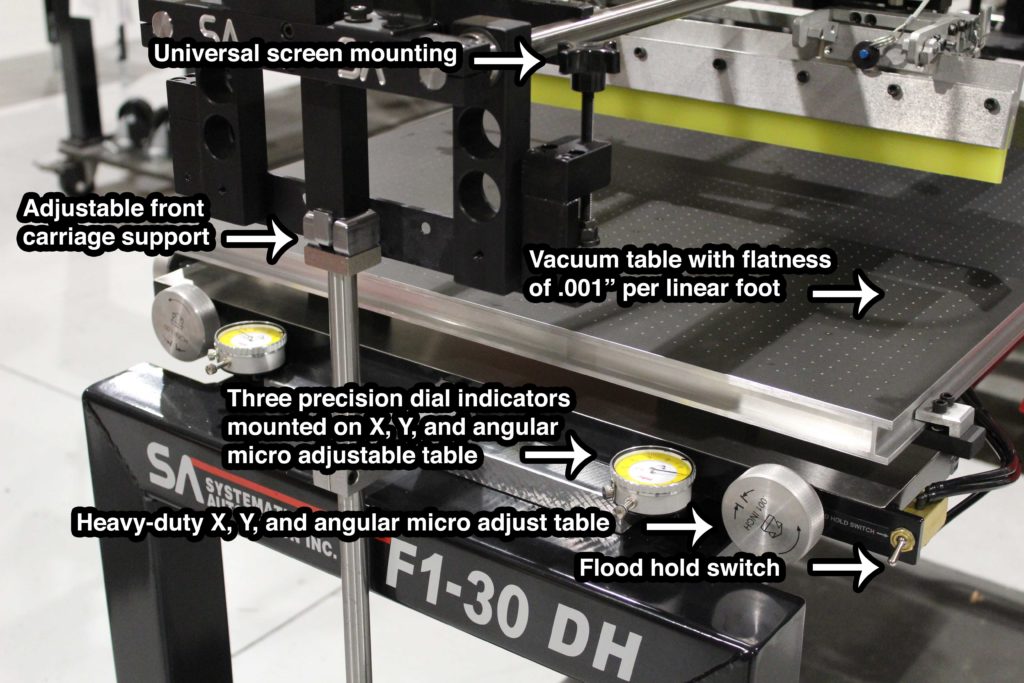
Systematic Automation: The Optimal Choice
In the realm of manufacturing, efficiency is paramount. Systematic automation emerges as the optimal choice for screen printing with conductive ink, offering unparalleled precision, consistency, and scalability. Automated systems streamline the printing process, minimizing human error and maximizing throughput—a critical factor in meeting the demands of mass production.
By integrating robotic arms, precision printers, and advanced control systems, automated manufacturing lines ensure the uniform deposition of conductive ink onto substrates with micron-level accuracy. This level of precision is essential, especially in applications where the performance and reliability of electronic components are paramount.
Furthermore, systematic automation enhances the reproducibility of printed electronics, facilitating seamless integration into large-scale production workflows. Whether it’s producing a batch of RFID tags or manufacturing flexible displays, automated systems ensure the consistent quality of printed components, meeting stringent industry standards and customer expectations.
Curing Conductive Inks: A Delicate Process
The curing of conductive inks is a critical step in the screen printing process, transforming liquid ink into solid, conductive traces. Unlike traditional inks, which rely on drying mechanisms, conductive inks typically require specialized curing methods to achieve optimal conductivity and adhesion to the substrate.
Various curing techniques are employed depending on the composition of the conductive ink and the properties of the substrate. Thermal curing, involving the application of heat to evaporate solvents and bond particles, is commonly used for inks based on silver, copper, or carbon. Ultraviolet (UV) curing, on the other hand, utilizes high-intensity UV light to polymerize the ink and create a durable, conductive layer.
The choice of curing method depends on factors such as substrate material, ink formulation, and production throughput. Each technique offers distinct advantages in terms of speed, energy efficiency, and compatibility with different substrates, allowing manufacturers to tailor the curing process to their specific requirements.
In conclusion, screen printing with conductive ink heralds a new era of innovation in electronics manufacturing. With its diverse applications, systematic automation, and intricate curing processes, conductive ink printing paves the way for the creation of smarter, more versatile electronic products. As technology continues to evolve, the possibilities offered by conductive ink printing are limited only by the bounds of imagination.